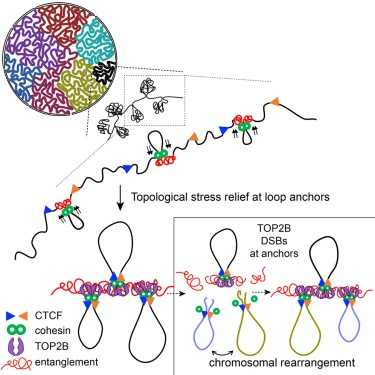
Functional Organization of Genome
The use of fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) has revealed that each chromosome occupies a distinct nuclear territory and that the 3D positioning of chromosomes correlates with chromosome size and gene density. “Think about it, where larger chromosomes should reside, where gene poor chromosomes can be, what kind of chromosomes should occupy centre of […]